Gold, a precious metal with historical significance, is highly valued for its use in jewelry, electronics, and as a financial asset. Its price is influenced by a multitude of factors, including economic conditions, geopolitical events, market demand, and supply dynamics. This article provides a detailed analysis of gold price trend, examining historical data, key factors driving price changes, and future outlooks.
Historical Price Trends
Long-Term Trends
Over the past several decades, gold prices have generally followed an upward trajectory. This long-term increase can be attributed to factors such as inflation, currency fluctuations, and increasing demand from both investors and industries. Gold is often seen as a safe-haven asset, attracting investors during times of economic uncertainty, which has also contributed to its rising value over the years.
Periodic Volatility
Gold prices are known for their periodic volatility, influenced by economic cycles, geopolitical events, and changes in market sentiment. Significant price fluctuations can be observed during financial crises, periods of high inflation, or geopolitical tensions. For instance, during the global financial crisis of 2008-2009, gold prices surged as investors sought safety amid economic turmoil.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/gold-price-trends/pricerequest
Key Factors Influencing Gold Prices
Economic Conditions
Inflation: Gold is often viewed as a hedge against inflation. When inflation rates rise, the value of currency typically declines, leading investors to buy gold as a store of value, which drives up its price.
Interest Rates: There is an inverse relationship between gold prices and interest rates. When interest rates are low, the opportunity cost of holding gold decreases, making it a more attractive investment. Conversely, higher interest rates can lead to lower gold prices as investors seek higher returns from other assets.
Currency Fluctuations: Gold prices are often inversely related to the value of the US dollar. When the dollar weakens, gold prices tend to rise as it becomes cheaper for investors holding other currencies. Conversely, a stronger dollar can lead to lower gold prices.
Market Demand
Investment Demand: Demand for gold as an investment, including gold ETFs (exchange-traded funds), bullion, and coins, plays a significant role in determining its price. Economic uncertainty, financial market volatility, and geopolitical risks often drive investment demand for gold.
Industrial Demand: Gold is used in various industries, including electronics, dentistry, and aerospace. Technological advancements and industrial growth can impact the demand for gold, influencing its price.
Jewelry Demand: Jewelry remains one of the largest uses of gold. Cultural and seasonal factors, such as wedding seasons in India and Chinese New Year, can drive significant demand for gold, affecting its price.
Supply Dynamics
Mining Production: The supply of newly mined gold affects its price. Factors such as mining costs, geopolitical stability in major mining regions, and regulatory changes can influence production levels and, consequently, gold prices.
Recycling: The recycling of gold from jewelry and other sources also contributes to supply. Economic conditions and gold prices can influence recycling rates, with higher prices typically leading to increased recycling activity.
Central Bank Policies: Central banks hold significant reserves of gold and can influence its price through their buying and selling activities. Policies regarding gold reserves can impact market supply and demand dynamics.
Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events, such as wars, trade disputes, and political instability, can drive investors to seek safety in gold. Such events often lead to increased demand and higher prices. For example, geopolitical tensions in the Middle East or trade disputes between major economies can create uncertainty, boosting gold prices.
Recent Price Trends
Short-Term Price Movements
In recent years, gold prices have experienced significant short-term fluctuations. For instance, in 2020, gold prices surged to record highs due to the economic uncertainty caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. Investors flocked to gold as a safe-haven asset, driving prices to unprecedented levels.
Impact of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on the gold market. The economic uncertainty and financial market volatility caused by the pandemic led to increased investment demand for gold. Additionally, disruptions in mining operations and supply chains affected the supply side of the market. These factors combined to drive gold prices to new heights in 2020.
Case Studies of Major Gold Markets
United States
The United States is a major player in the global gold market, both as a producer and consumer. The US dollar's strength and monetary policy significantly influence gold prices. For instance, the Federal Reserve's actions regarding interest rates and quantitative easing programs can impact gold demand and prices.
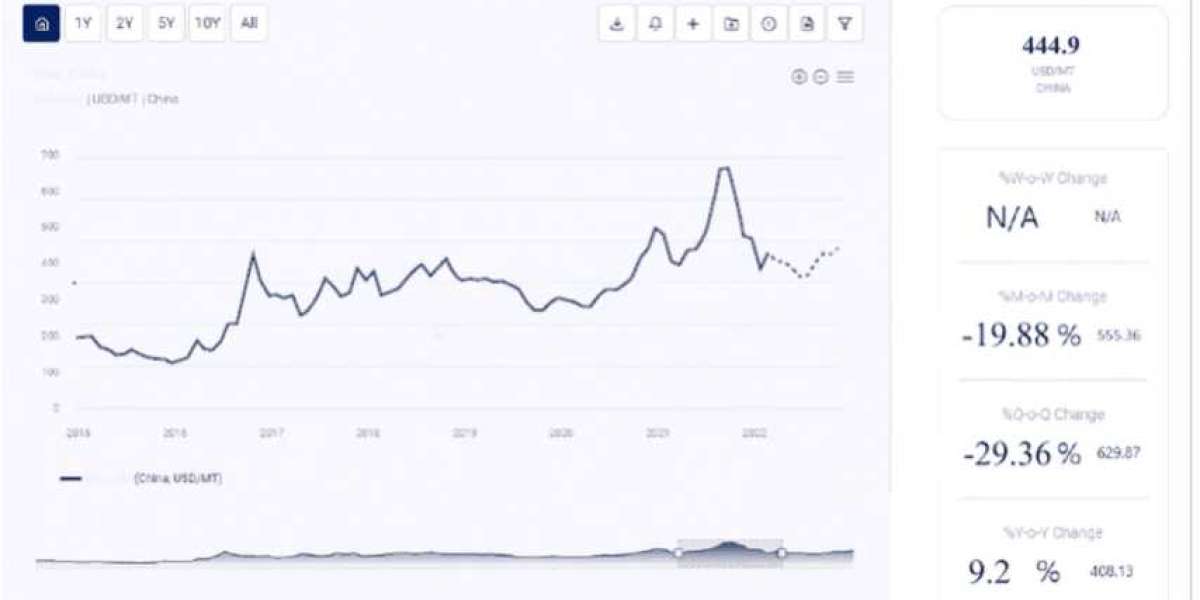
China
China is one of the largest consumers and producers of gold. The country's demand for gold jewelry and investment products plays a crucial role in global gold prices. Additionally, China's central bank policies regarding gold reserves can influence market dynamics.
India
India is another significant market for gold, particularly for jewelry. Cultural factors and seasonal demand, such as during the wedding season and festivals like Diwali, drive substantial gold purchases. Economic conditions and import policies in India also affect gold prices.
The Impact of Climate Change on Gold Production
Climate change poses risks to gold production globally. Changes in temperature, precipitation patterns, and the frequency of extreme weather events can impact mining operations. Key impacts of climate change on gold production include:
Resource Availability: Changes in climate conditions can affect the availability of water and energy resources required for mining operations. Droughts, floods, and other extreme weather events can disrupt mining activities and increase production costs.
Regulatory Changes: Governments may implement stricter environmental regulations to combat climate change, impacting mining costs and operations. Policies promoting sustainable mining practices and reducing carbon emissions can influence gold production.
Sustainability Initiatives: The gold industry is increasingly focusing on sustainability initiatives, such as reducing carbon emissions and promoting responsible mining practices. These initiatives can affect production costs and market dynamics.
Technological Innovations in Gold Production
Technological advancements are transforming the gold industry, offering solutions to some of the challenges faced by producers. Key innovations include:
Energy Efficiency: Advances in energy-efficient mining technologies can reduce production costs and carbon emissions. Technologies such as renewable energy integration and energy-efficient processing methods can improve the sustainability of gold production.
Automation and Digitalization: The adoption of automation and digitalization in mining operations can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance supply chain resilience. Technologies such as automated drilling, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance can streamline operations and reduce waste.
Recycling Technologies: Improved recycling technologies can increase the supply of secondary gold, reducing the need for primary production and lowering environmental impact. Innovations in extraction and refining processes can enhance the efficiency of recycling operations.
Future Outlook
Demand Growth
The demand for gold is expected to remain strong, driven by factors such as economic uncertainty, inflation concerns, and increasing industrial and jewelry demand. Emerging markets, particularly in Asia, are expected to be major drivers of future demand. Additionally, the shift towards sustainable and responsible investment practices may boost demand for ethically sourced gold.
Supply Challenges
Supply challenges, including resource availability, environmental regulations, and production costs, will continue to impact gold prices. Ensuring a stable supply of gold and adopting sustainable production practices will be critical for the industry. Investments in mining technology and recycling infrastructure will help mitigate supply risks.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements will play a key role in shaping the future of the gold industry. Innovations in energy efficiency, recycling, and automation will help producers meet growing demand while addressing environmental and cost challenges. Continued investment in research and development will be essential for maintaining competitiveness and sustainability.
Conclusion
Gold prices are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including economic conditions, market demand, supply dynamics, and geopolitical events. Understanding these factors is essential for stakeholders across the gold supply chain, from producers to investors and policymakers. By adopting sustainable practices, investing in technology, and implementing effective policy interventions, it is possible to mitigate price volatility and ensure a stable supply of this precious metal. As global challenges like climate change continue to evolve, the gold industry must adapt to maintain the delicate balance between supply and demand, ensuring that gold remains a valuable and accessible asset for various applications worldwide.